Andrea Silverman
Generative Motion, Visual Effects, and Spatial Systems Exploration
I develop high-fidelity HUD, motion graphics, and spatial UI systems that translate cinematic visual language into real-time XR prototypes. My workflows combine After Effects–grade VFX, procedural motion patterns, and advanced compositing with Quest 3/Pro’s depth-aware passthrough and interaction stack. I build motion systems engineered for stability, clarity, and visual impact—anchored to real surfaces, gaze-responsive, and optimized for jitter, occlusion, and variable lighting.
Drawing from experience validating Microsoft Mixed Reality devices and creating AI-driven animation systems at Meta, I deliver visually rich, technically robust sequences that scale across both offline pipelines (AE, Blender) and real-time engines (Unity/Unreal). I specialize in precision keyframing, motion studies, visual effects design, and multi-layer HUD animation that feels film-quality yet runs in mixed reality.
My work supports end-to-end VFX prototyping: concept → motion design → compositing → interaction pass → final integration. This page highlights motion-driven HUD systems, XR-ready UI animation patterns, and AI-enhanced visual effects aligned with the expectations of a senior-level Technical Artist role.
Focus Areas:
-
AI-enhanced visual effects and motion generation
-
adaptive HUD + spatial UI for mixed reality
-
real-time MR compositing and depth-aware rendering
-
multimodal interaction (gesture, voice, gaze)
-
concept-to-prototype pipelines for XR products
-
user flow design for spatial interaction systems
-
LLM-driven contextual reasoning and feedback
-
rapid iteration for early-stage R&D
This page represents my R&D sandbox — where I prototype, evaluate, and evolve the next wave of VFX, XR, and AI-driven interaction systems for mixed reality.




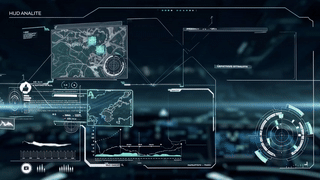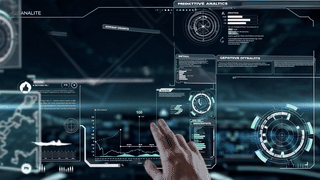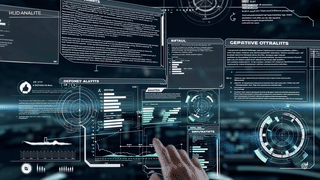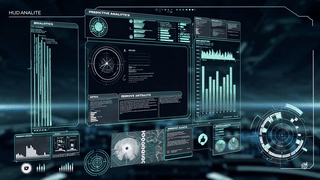

Next-Gen HUD System & Suit Interface (Astraeon Project)
Skills: VFX language, UI animation patterns, HUD motion, spatial systems design, Quest MR design, multimodal interaction, AI-driven UI adaptation
Tech Used: Meta Quest 3 / Quest Pro, Passthrough MR, Presence Platform, Scene Understanding, OpenXR, Meta’s Hand Tracking 2.5, Meta Movement SDK, Unity (XR pipeline), Blender, After Effects, Photoshop
Summary:
Astraeon explores a cinematic HUD vocabulary for MR: glowing depth-layered UI, parallax-driven motion cues, real-time environmental compositing, and gesture-triggered transitions built to read clearly in passthrough. The interface uses VFX principles—dynamic glows, volumetric direction markers, inertia-based easing curves, peripheral flares, and color-coded telemetry rings—to communicate urgency and scale at a glance. Designed with motion fidelity, occlusion accuracy, and real-world lighting in mind, Astraeon brings cinematic language into a functional, spatially-anchored MR system.
Description:
Astraeon is a next-generation MR HUD prototype built on Meta Quest hardware, designed to anchor mission-critical information into the real world through depth-aware UI, adaptive gaze-driven layout, intuitive gesture workflows, and lightweight AI-assisted spatial reasoning. This system blends VFX precision, XR interaction design, and real-time spatial computing to demonstrate how future interfaces can support humans in extreme, fast-moving, or cognitively demanding environments.
Key elements:
1. Real-World Anchored HUD (Meta Quest MR)
-
Stable passthrough overlays that lock to surfaces and respect occlusion
-
Clear, readable UI in any lighting condition
2. Adaptive UI Driven by Gaze + Head Pose
-
HUD layout reflows based on where the user is looking
-
Reduces cognitive load and keeps critical info in view
3. Gesture-Driven Interaction (Hand Tracking 2.5)
-
Micro and macro hand gestures for navigation and control
-
Hands-free operation designed for gloved or restricted environments
4. AI-Assisted Spatial Context Layer
-
Highlights hazards, summarizes telemetry, and surfaces key signals
-
Combines voice and gesture input for multimodal control
5. Depth-Aware Navigation & Spatial Markers
-
Trajectory paths, markers, and vitals rendered at true spatial depths
-
Improves distance judgment and situational clarity
6. MR-Optimized Motion Language
-
Motion communicates urgency, distance, and status
-
Designed for fast perception in high-demand scenarios
Interactions emphasize gesture-driven navigation, hands-free controls, and motion patterns engineered for low-gravity readability.
Tactical Command HUD & Spatial UI System
Skills: system mapping, XR-ready UI, UI architecture, diagramming
Tech Used: Figma, After Effects, Blender
Summary:
A spatial interface designed for command operations where rapid decision-making and predictive awareness are critical.
Description:
This system aggregates multiple data streams into a tactical UI where operators can anticipate hazards, track threat trajectories, and identify priority zones.
The UI is built around modular components that adapt to XR simulation environments, enabling both training and real-time command scenarios.
The project highlights diagram-driven UX logic and motion-informed interface patterns.
Design Lineage & Technical Inspiration
My HUD and spatial UI methodologies are shaped by hands-on engineering and testing experience from Microsoft Mixed Reality and current-generation Meta Quest hardware. At Microsoft, I validated device performance across passthrough stability, environmental understanding, and real-world readability—direct experience that now informs my approach to building robust, low-jitter, depth-anchored motion language on Quest 3/Pro.
These learnings translate into systems optimized for real-time MR constraints:
stable anchoring, adaptive motion weighting, gaze-aware UI placement, and mission-ready interaction patterns designed for reliability under real-world conditions.

Adaptive XR Training Prototype (Mixed Reality)
Skills: XR UI architecture, system mapping, adaptive interfaces, motion cues
Tech Used: Unity (MR Toolkit), VFX Graph, Blender, PyTorch (adaptive logic prototypes)

Summary:
A training simulator that adapts its HUD, feedback patterns, and interface behaviors based on user proficiency and mission context.
Description:
Drawing inspiration from my work in Microsoft Mixed Reality’s Defense division, this prototype explores how XR systems evolve dynamically as operators build their skills.
The interface incorporates AI-driven difficulty scaling, multi-sensory feedback, and real-time analytics, resulting in a training environment that becomes increasingly personalized and effective over time.
No two operators experience the same HUD — the system grows with the user.


AR Windshield Interface
Skills: HUD motion language, spatial UI design, VFX animation, XR UI architecture, depth-aware rendering, gaze/gesture interaction, real-time prototyping
Tech Used: Meta Quest 3/Pro/Pro 2 (HDR passthrough), Presence Platform 2.5 (Scene Understanding v3, Semantic Mesh, Hand Tracking 2.5, Eye Input APIs, World Anchors 2.0), Unity XR, After Effects, Blender, Meta Multimodal AI, OBD-II/Tesla API simulators
Summary:
A next-gen AR windshield HUD that transforms real driving environments into a depth-stable, gaze-adaptive, gesture-responsive interface. Built on Meta Quest’s 2025 MR stack, this prototype visualizes navigation, safety cues, ADAS intelligence, and environmental context with cinematic motion design—anchored directly to the world outside the car.
Description:
Powered by HDR passthrough and Scene Understanding v3, the HUD places arrows, cones, and safety indicators directly onto the road with accurate occlusion and depth. Semantic Mesh identifies vehicles, lanes, pedestrians, and sky, enabling context-aware alerts.
-
The interface adapts with gaze-responsive layout shifts—important data moves inward when needed, while secondary elements drift to the periphery.
-
Hand Tracking 2.5 and Movement SDK enable pinch, swipe, and palm gestures to change modes or expand telemetry without touching a screen.
-
Meta’s multimodal AI summarizes hazards, forecasts safe paths, annotates the environment, and adjusts visual weighting based on weather, speed, and cognitive load.
-
All animations use a cinematic VFX motion language optimized for MR stability—low jitter, glow-weighted signals, volumetric arrows, and parallax cues that remain readable under vibration or glare.
A depth-stable, AI-enhanced mixed-reality HUD — powered by Meta Quest and built for real-world driving clarity.



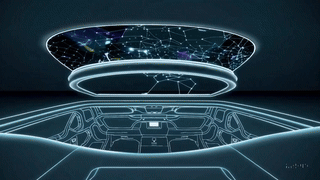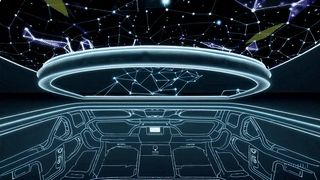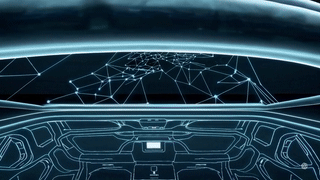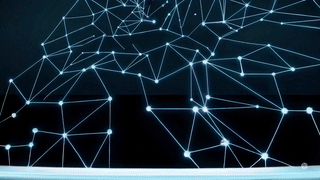
Luma Roof — API-Connected Holographic Moonroof
A living digital sky designed for calm, creativity, and immersive motion.
Skills: HUD motion language, spatial UI design, VFX animation, XR UI architecture, depth-aware rendering, gaze/gesture interaction, real-time prototyping
Tech Used: Meta Quest 3/Pro/Pro 2 (HDR passthrough), Presence Platform 2.5 (Scene Understanding v3, Semantic Mesh, Hand Tracking 2.5, Eye Input APIs, World Anchors 2.0), Unity XR, After Effects, Blender, Meta Multimodal AI, OBD-II/Tesla API simulators
Summary:
Luma Roof transforms the vehicle interior into an ambient, holographic environment that responds to weather, music, motion, and user gestures.
Part celestial canvas and part biophilic sanctuary, it blends generative visuals, adaptive lighting, and real-time data inputs to create an experience that feels alive—day or night.
Core Experience
-
Celestial + nature-inspired effects that create a calm, restorative environment
-
Ambient overlays that shift with time, location, and weather
-
Music-reactive animations driven by BPM, genre, and emotional tone
-
AI-generated artwork that evolves with each drive
-
Gesture-based interactions for intuitive theme control
-
Biophilic design meets digital expression



AI-Enhanced AR Companion (LLM-Based Interaction)
Skills: AR scanning, LLM integration, flow diagrams, contextual UX
Tech Used: Unity (AR Foundation), ARKit/ARCore, OpenAI GPT APIs, Google Speech-to-Text, REST/Socket APIs
Summary:
A context-aware AR assistant that answers user questions about real-world objects using LLMs and voice-based interaction.
Description:
Users scan an object (such as a painting or sculpture), and the system uses AR object detection to identify it. A built-in LLM processes user questions and delivers conversational, adaptive responses directly in AR. The project includes a fully diagrammed user flow outlining scanning, querying, processing, and response cycles.
This demonstrates how AI and spatial computing can merge into a dynamic educational companion.
User Flow Diagram Outline:
